You’re scrolling through social media and see a post claiming a “hot stock tip” that’s guaranteed to skyrocket. Suddenly, every financial news article you read seems to mention that same company. You feel excitement – this must be the next big thing!
According to the principles of behavioral finance:
“Investment is 80% psychology.”
You quickly place a trade, ignoring the nagging voice in the back of your head that reminds you to do more research.
Unfortunately, this scenario often plays out in the fast-paced trading industry. We humans are not the perfectly rational actors traditional financial models assume us to be.
Our decisions are heavily influenced by psychological factors and mental shortcuts, often leading to less-than-optimal outcomes. This is where the field of behavioral finance steps in.
Behavioral finance bridges the gap between psychology and economics, specifically focusing on how emotions and cognitive biases impact financial decisions. It challenges the traditional view of the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH), which assumes markets are perfectly efficient and reflect all available information.
The reality is that financial markets are filled with real people, susceptible to various cognitive biases.
Understanding these biases is crucial for successful trading. By recognizing how our minds can trick us, we can make more informed decisions and potentially avoid costly mistakes.
Just like a skilled athlete studies their opponent’s weaknesses, a successful trader needs to understand the biases working against them.
Acknowledging these mental roadblocks allows you to develop strategies to overcome them and navigate the ever-changing market landscape more clearly.
What Are Cognitive Biases?
Our brains are constantly bombarded with information. To cope with this overload, we rely on mental shortcuts called heuristics. These heuristics are often helpful, allowing us to make quick decisions in everyday life. However, these shortcuts can sometimes lead us astray in the complex world of financial markets.
Cognitive biases are systematic errors in thinking that distort our judgment and influence our behavior. They can cloud our ability to process information objectively and lead to poor financial decisions.
What do you think how cognitive biases can impact your financial decisions?
They can lead to emotional decision-making. Fear, greed, and overconfidence can all cloud our judgment and cause us to make impulsive trades based on emotions rather than logic.
They can limit our ability to consider all available information. Confirmation bias, for example, can lead us to seek information confirming our existing beliefs and ignore evidence that contradicts them.
They can make us overestimate our abilities. Overconfidence bias can lead us to believe we are better investors than we truly are, potentially leading to riskier trades and larger losses.
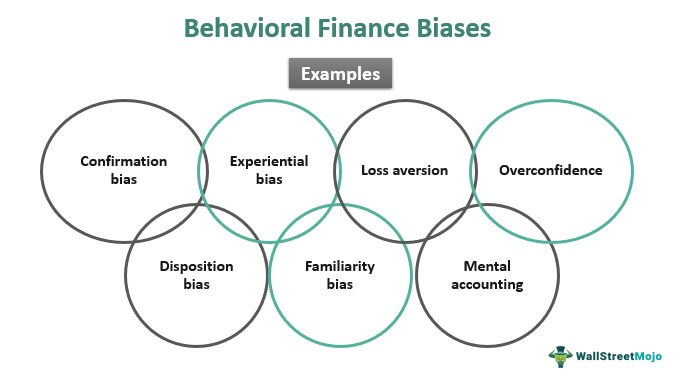
Two main categories of cognitive biases influence financial decisions:
1 – Emotional Biases
Our emotions and feelings drive these biases. Some common examples include:
Loss aversion – The tendency to feel the pain of losing money more intensely than the pleasure of gaining the same amount. This can lead to holding onto losing positions too long and selling winning positions too early.
Fear of missing out (FOMO) – The feeling of anxiety or regret that we might miss out on a profitable opportunity. This can lead to chasing hot stocks or investing in risky ventures without proper research.
Anchoring bias – The tendency to rely too heavily on the first piece of information we receive when making a decision. This can lead to making investment decisions based on irrelevant information, such as the initial price of a stock.
2 – Cognitive Errors
These biases are rooted in limitations in how our brains process information. Some common examples include:
Confirmation bias – The tendency to seek information confirming our beliefs and ignore evidence that contradicts them. This can lead to making investment decisions based on flawed information.
Mental accounting – The tendency to categorize money into different mental accounts can lead to making suboptimal investment decisions. For example, you might be more willing to invest a windfall than your regular savings.
Overconfidence bias – The tendency to overestimate our skills and knowledge, leading to risky investment decisions.
The Common Cognitive Biases In Trading
The battleground of financial markets is littered with mental traps waiting to ensnare unsuspecting traders. Here are some of the most common cognitive biases that can wreak havoc on your trading decisions:
1. Confirmation Bias
Imagine you’re convinced a particular stock is about to take off. Suddenly, every news article you read seems to point towards its potential. This is confirmation bias in action. We naturally gravitate towards information confirming our beliefs, conveniently ignoring any evidence contradicting them.
2. Loss Aversion
The sting of losing feels far worse than the joy of winning the same amount. This aversion to losses can lead to a cascade of bad decisions.
3. Overconfidence Bias
We all have a healthy dose of self-belief, but sometimes it inflates into overconfidence. This bias leads us to overestimate our skills and knowledge, potentially leading to disastrous consequences in the market.
4. Anchoring Bias
The first piece of information we encounter can have an outsized influence on our decisions. This anchoring bias can lead to suboptimal choices in the fast-paced trading world.
5. Disposition Effect
This bias describes our tendency to sell winning positions too early and cling to losing ones for too long. We get attached to winning stocks, fearing losing out on further gains if we sell. Conversely, we hold onto losing positions, hoping they’ll eventually recover, even when all evidence suggests otherwise.
More Biases to Consider
- Recency Bias – We tend to place more weight on recent events, potentially overlooking long-term trends.
- Framing Bias – The way information is presented can greatly influence our decisions.
How To Overcome Cognitive Biases?
If you want to conquer cognitive biases in trading, you need to consider multiple options. The first line of defense is self-awareness. By recognizing how these biases might influence your decisions, you can start detaching from emotional impulses.
Develop a trading plan that outlines clear entry and exit points, risk management strategies, and investment goals. This plan serves as a roadmap, guiding decisions based on logic rather than fleeting emotions.
Besides, you can add trade bots to your plan so that these bots can be your eyes in the market. Tools like Quantum AI help traders by monitoring the market, recording price fluctuations, and providing live market analysis.
They can offer some advantages but shouldn’t be a primary solution. Markets are complex and ever-changing, and relying solely on bots can be risky.
Diversification is another powerful weapon. Spreading your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and commodities, helps mitigate risk and reduces the impact of any single bias on your portfolio.
To combat confirmation bias, actively seek diverse information sources. Read financial news critically, considering viewpoints that contradict your own.
Finally, employ reality checks. Regularly evaluate your trades, assess your performance against your plan, and adjust your strategies as needed. This ongoing self-evaluation process is key to mitigating the influence of cognitive biases and navigating the market with greater clarity and discipline.
Wrapping Up
The fight against cognitive biases is an ongoing battle. These mental shortcuts are deeply ingrained, and their influence can be subtle. However, you can become a more mindful and disciplined trader by wielding the tools of self-awareness, strategic planning, and continuous learning.
Remember, the market is a formidable opponent, and constant vigilance is essential to outsmart your biases and achieve long-term trading success.