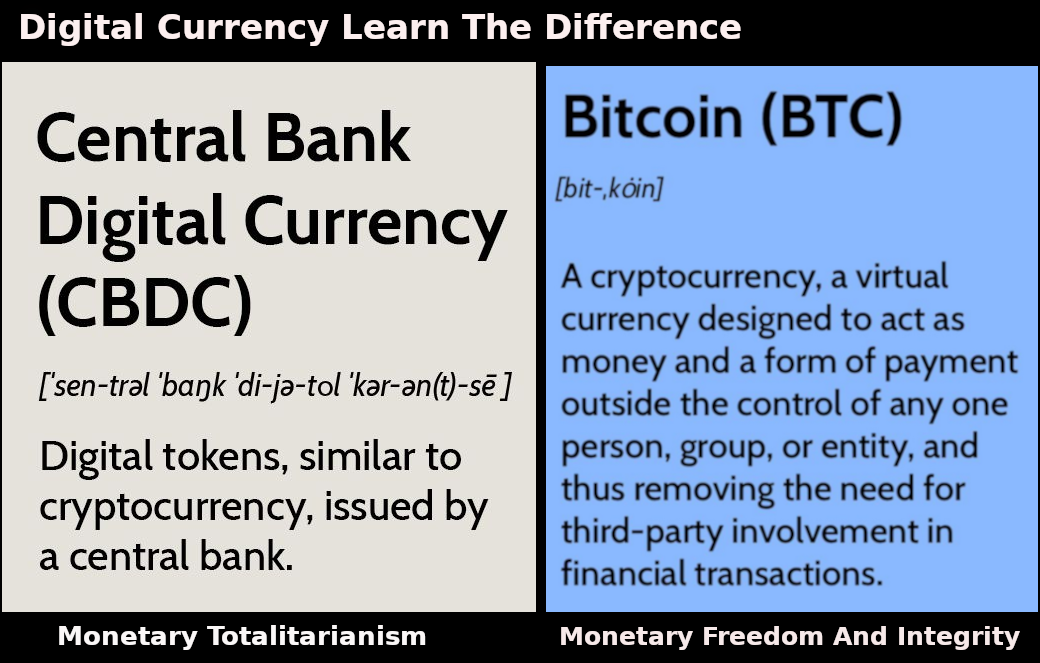
Cryptocurrency has been gaining immense popularity in recent times, with people looking to diversify their investments and guard against the volatility of traditional currencies. Two of the most popular digital currencies are Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and Bitcoin. Both offer a range of benefits, and this article will look at the differences between them, to help you decide which one is right for you. CBDCs are digital currencies issued by central banks or other financial authorities, while Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency with no central control or authority. Both have their own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to understand the differences between them before making a decision.
Overall, CBDCs and Bitcoin are very different digital assets. CBDCs are issued and regulated by a central authority, while Bitcoin is decentralized and not subject to any government or central bank control. CBDCs offer the potential for faster and cheaper payments, but lack the privacy and security that Bitcoin offers. Ultimately, the choice of which digital asset to use and how it will be used is up to the individual or business.

Exploring the Possibilities of CBDCs as a Payment Method vs. Bitcoin
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are a type of digital currency created and regulated by a central bank or other authority. CBDCs provide a secure, digital payment method that is designed to be as efficient and cost-effective as possible. The technology behind CBDCs is similar to that of Bitcoin, but with some key differences. CBDCs are issued and regulated by a central bank or other government authority. This means that, unlike Bitcoin, the value of a CBDC is not subject to market fluctuations and is backed by a reliable and secure source. Additionally, CBDCs are designed to be faster and more cost-effective than traditional payment methods, as they can be sent and received instantly and without the need for intermediaries. Another major difference between CBDCs and Bitcoin is that Bitcoin is not regulated by any government or central bank. This means that the value of Bitcoin is heavily dependent on market forces, making it prone to volatility. Additionally, Bitcoin transactions are not always secure, as the underlying technology is vulnerable to hacking and theft. In contrast, CBDCs are highly secure and reliable, as they are issued and regulated by a government or central bank. This offers greater protection for users, as the currency is backed by a reliable source. Additionally, CBDCs can be sent and received instantly, making them a more efficient payment method than Bitcoin. In conclusion, CBDCs offer a secure and cost-effective payment method that is far more reliable than Bitcoin. Although Bitcoin offers some advantages, such as its decentralized nature, its lack of regulation makes it vulnerable to market fluctuations, while its underlying technology is vulnerable to hacking and theft. For these reasons, CBDCs are often seen as a more secure and reliable option.
Is a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) the Future of Money?
As financial technology continues to evolve and transform, the concept of a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) has been gaining traction in recent years. A CBDC is a type of digital representation of a country’s fiat currency, issued and backed by a Central Bank. The idea of a CBDC has the potential to revolutionize the way money is used and managed, but is it really the future of money? To answer this, it is important to consider the potential advantages of a CBDC. For starters, a CBDC could make the payments system faster, more efficient and secure. Transactions could be completed in a matter of seconds and be more secure due to higher levels of encryption and authentication. Furthermore, a CBDC could reduce transaction costs for both businesses and consumers, meaning more money could stay in people’s pockets instead of being lost in the payment system. A CBDC could also lead to increased financial inclusion and access to financial services. By providing an alternative to cash and traditional banking services, it could help those who are currently excluded from the banking system access banking services and open up new opportunities, especially in developing countries. Finally, a CBDC could be a powerful tool for governments to control and manage the money supply and have greater oversight into the economy. This could help prevent financial crises, as the impact of any shocks to the economy could be mitigated. Given the potential advantages of a CBDC, it is clear that it could be an important tool for the future of money. However, it is important to recognize that there are a number of challenges that need to be overcome before a CBDC can be implemented. These include ensuring the security and privacy of transactions, developing the necessary infrastructure, and ensuring that the system is compliant with current laws and regulations. Overall, it is clear that a CBDC could be an important tool for the future of money. However, to make the transition from concept to reality, there are a number of challenges that need to be overcome. Only time will tell if a CBDC is truly the future of money.
How Do CBDCs and Bitcoin Compare in Terms of Security and Privacy?
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are both digital assets that have grown in popularity over the past decade. While they share some similarities, they also have significant differences when it comes to security and privacy. Security wise, both Bitcoin and CBDCs offer a secure way to store, transfer and spend money. Bitcoin uses a blockchain to record transactions, while CBDCs may use a distributed ledger technology. Both systems are designed to prevent any potential fraud or double spending. Bitcoin also has a network of miners who serve as its auditors, verifying each transaction and ensuring its accuracy. CBDCs may use a different system to ensure its security, but the security of both systems is generally considered to be very high. When it comes to privacy, Bitcoin is seen as a more private system. Transactions are recorded on the blockchain, but the identity of the sender and receiver are kept anonymous. This makes it difficult for anyone to trace the origin of the funds or track the movements of the users. On the other hand, CBDCs may not offer the same level of anonymity as Bitcoin. This is because, in most cases, CBDCs would require users to register with the central bank and provide personal information. This makes it easier for the government to track the user’s transactions. Overall, while both Bitcoin and CBDCs offer a secure way to store, transfer, and spend money, their levels of security and privacy can vary depending on their design. Bitcoin is generally seen as more private, while CBDCs may be more transparent. Therefore, it is important to understand the differences before making a decision on which system to use.
What Are the Regulatory Implications of CBDCs and Bitcoin?
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and Bitcoin are emerging technologies that have been met with both enthusiasm and trepidation. While they offer the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with money and financial services, they also bring with them a host of regulatory implications. One of the main implications of CBDCs is the potential for increased financial inclusion. By providing the public with access to digital central bank money, CBDCs can help those who are currently excluded from the traditional financial system to access the same financial services as those with more access to financial resources. Moreover, CBDCs have the potential to reduce the cost of financial services for all consumers, as well as to facilitate cross-border payments and remittances. The regulatory implications of Bitcoin are more complex. As an unregulated asset, Bitcoin can be used for a variety of illicit activities, such as money laundering and tax evasion. In response, governments around the world have sought to regulate Bitcoin in various ways. In some cases, this has taken the form of introducing registration and reporting requirements for cryptocurrency exchanges and other entities operating in the space. In other cases, governments have sought to impose bans on the use of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies. Finally, it is important to note that both Bitcoin and CBDCs have the potential to disrupt the existing financial system. This could lead to significant changes in the way banks, financial institutions, and other stakeholders operate and interact with one another. As such, governments and regulators will need to remain vigilant in monitoring the development of these technologies and the implications for the financial system. In conclusion, the regulatory implications of CBDCs and Bitcoin must be carefully considered by governments and regulators around the world. By doing so, they can ensure that these technologies are used responsibly and in a manner that benefits society as a whole.
The Pros and Cons of CBDCs vs. Bitcoin
The debate over the merits of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) versus Bitcoin has been ongoing for some time. Both have their pros and cons, and understanding these can help inform decisions on which is best suited to any given situation. Pros of CBDC One of the main advantages of CBDC is that it is backed by a central authority. This means that the currency is more secure and reliable, as it is subject to the oversight and regulation of the issuing authority. Additionally, CBDCs can be exchanged for fiat currency, and can be used for a variety of purposes, including international payments and remittance. CBDCs are also more accessible than Bitcoin, as they can be accessed through online banking platforms or through an app. This means that they are more user-friendly and can be used with ease by those who may not be familiar with cryptocurrencies. Lastly, CBDCs have the potential to provide greater financial inclusion, as they can be used by people who are currently excluded from the traditional banking system. This could help to reduce poverty and inequality, as well as providing more access to financial services. Pros of Bitcoin Bitcoin is a decentralised currency, and therefore it is not subject to the control of any central authority. This makes it resistant to inflation and censorship, as it is not tied to any particular country or government. Additionally, Bitcoin is incredibly secure, and its transactions are irreversible. This means that it is difficult for hackers or fraudsters to access or manipulate Bitcoin transactions. Bitcoin is also highly anonymous, and transactions do not require the exchange of personal information. This makes it ideal for those who want to remain anonymous when conducting their financial activities. Additionally, Bitcoin’s low transaction fees make it an attractive option for those who wish to make low-cost transfers. Furthermore, Bitcoin can be used for a variety of purposes, such as investing, trading, and making purchases. This gives it more versatility than CBDCs, and makes it a viable alternative to traditional currencies. Conclusion Both CBDCs and Bitcoin have their pros and cons, and it is up to the individual to decide which is best suited to their particular needs. CBDCs have the advantage of being backed by a central authority, but they will be used to control every human possible. In conclusion, CBDCs are monetary totalitarianism