A DDoS attack can severely compromise the security of a blockchain network by taking down nodes and bloating the network with fraudulent transactions.
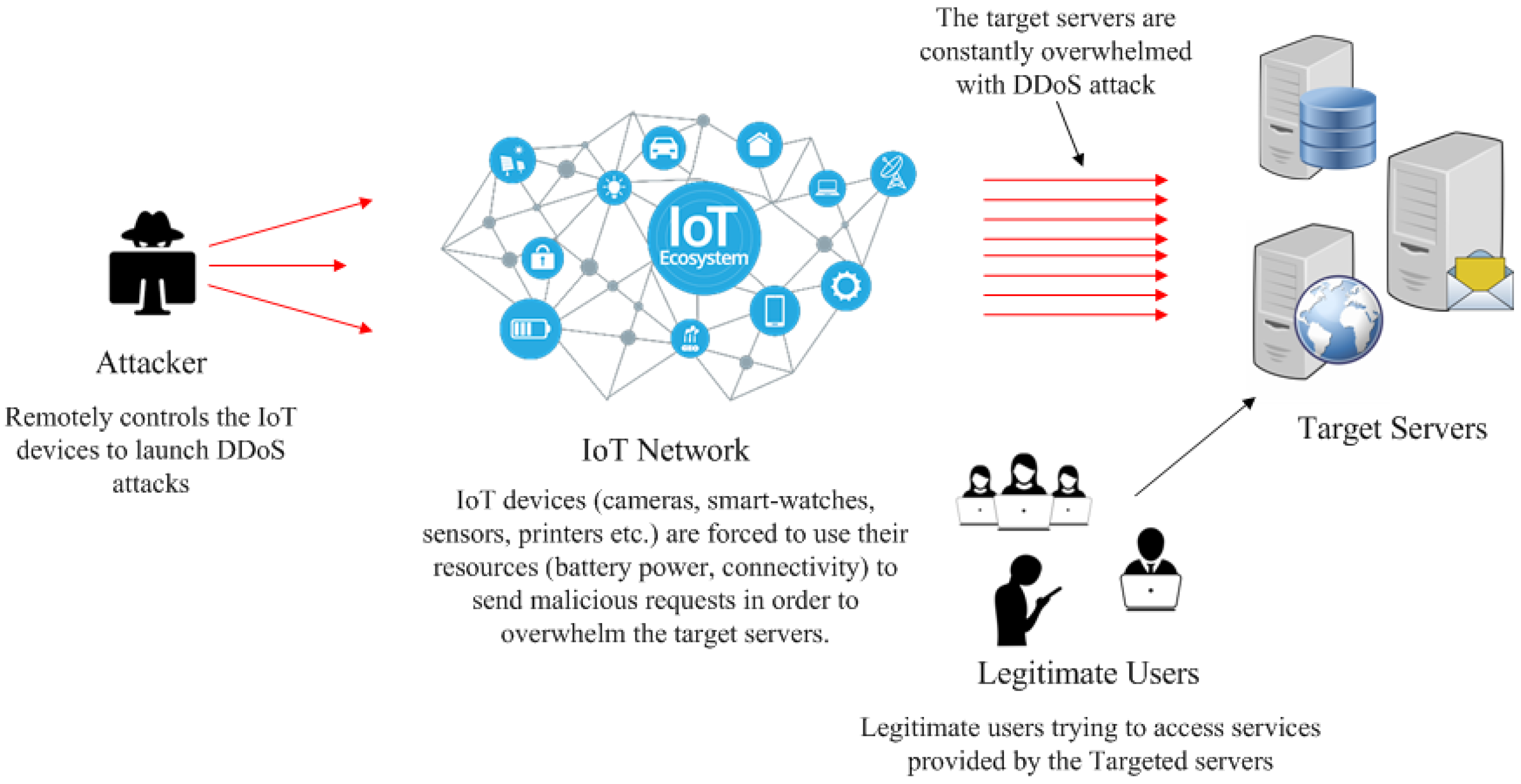
A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack attempts to take down a website, computer or online service by flooding it with requests, depleting its capacity and affecting its ability to respond to valid requests.
A DDoS attack involves hackers inserting malware into possibly thousands of internet-enabled devices, collectively referred to as a botnet, and prompting them to deliver a deluge of requests to the target system simultaneously. These compromised machines, individually termed bots or zombies, could be cellphones, desktops, servers or even Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Attackers usually establish direct control over bots by infecting them with malware without the knowledge of the victims.