Facial recognition technology, hailed for its convenience and security applications, is under increased scrutiny due to its failure to accurately identify individuals, particularly people of color. Recent reports have highlighted instances where facial recognition systems misidentified individuals, leading to privacy infringement and discrimination concerns. These issues are prompting calls for reassessment and potential rollbacks in its widespread use.
Racial bias in facial recognition technology
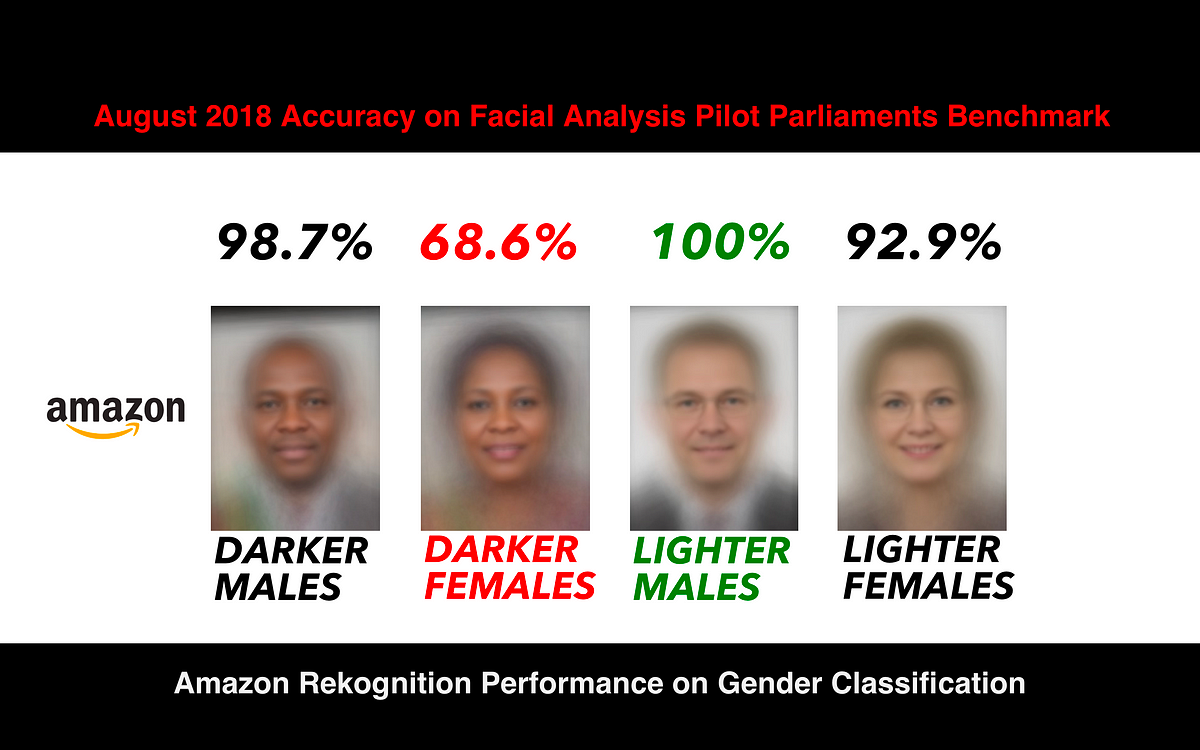
One of facial recognition technology’s most pressing concerns is its racial bias. Studies have shown that these systems are significantly less accurate in identifying people of color compared to white individuals. MIT Media Lab researcher Joy Buolamwini’s 2018 study found that facial recognition technology misidentified black women up to 35% of the time, while white men were misidentified in just 1% of cases. Similarly, a federal study in 2019 concluded that Asian, African-American individuals and women were more likely to be falsely identified than white men.
The root cause of this bias lies in the disproportionate representation of white individuals in the datasets used to train facial recognition algorithms. With fewer images of people from diverse racial and gender groups, these systems lack the necessary accuracy to correctly identify individuals from these backgrounds. As a result, people of color are disproportionately impacted by the inaccuracies of facial recognition technology.
The ramifications of facial recognition technology’s inaccuracies extend beyond mere inconvenience. Instances of misidentification can lead to serious consequences, particularly in security-sensitive environments such as airports and retail establishments. Reports indicate that individuals have been wrongfully denied access or services due to facial recognition systems falsely flagging them.
Moreover, concerns about privacy infringement are heightened as these systems become more pervasive. The reliance on facial recognition for identity verification raises questions about protecting personal data and the potential for unauthorized surveillance. Critics argue that the widespread adoption of facial recognition technology without adequate safeguards threatens civil liberties and exacerbates existing inequalities.
Calls for reevaluation and regulation
In light of these issues, there are growing calls for reevaluation and regulation of facial recognition technology. Critics argue that the potential benefits of these systems must be weighed against their significant drawbacks, including racial bias and privacy concerns. Some advocates are calling for stricter oversight and transparency requirements to ensure accountability in developing and deploying facial recognition technology.
Furthermore, there is a push for greater diversity in the datasets used to train these systems to mitigate racial bias. By incorporating more images of people from diverse backgrounds, facial recognition algorithms can improve their accuracy and reduce the risk of misidentification. Additionally, there are calls for companies and government agencies to provide alternatives to facial recognition for individuals who prefer not to use or are adversely affected by the technology.
Facial recognition technology’s widespread adoption has brought convenience and efficiency to various industries, but concerns about its accuracy and racial bias cannot be ignored. As reports of misidentification and privacy infringements continue to surface, there is a pressing need for reevaluation and regulation. Stricter oversight, greater diversity in training datasets, and alternative options for identity verification are essential steps toward addressing these issues and ensuring that facial recognition technology is used responsibly and ethically in the future.