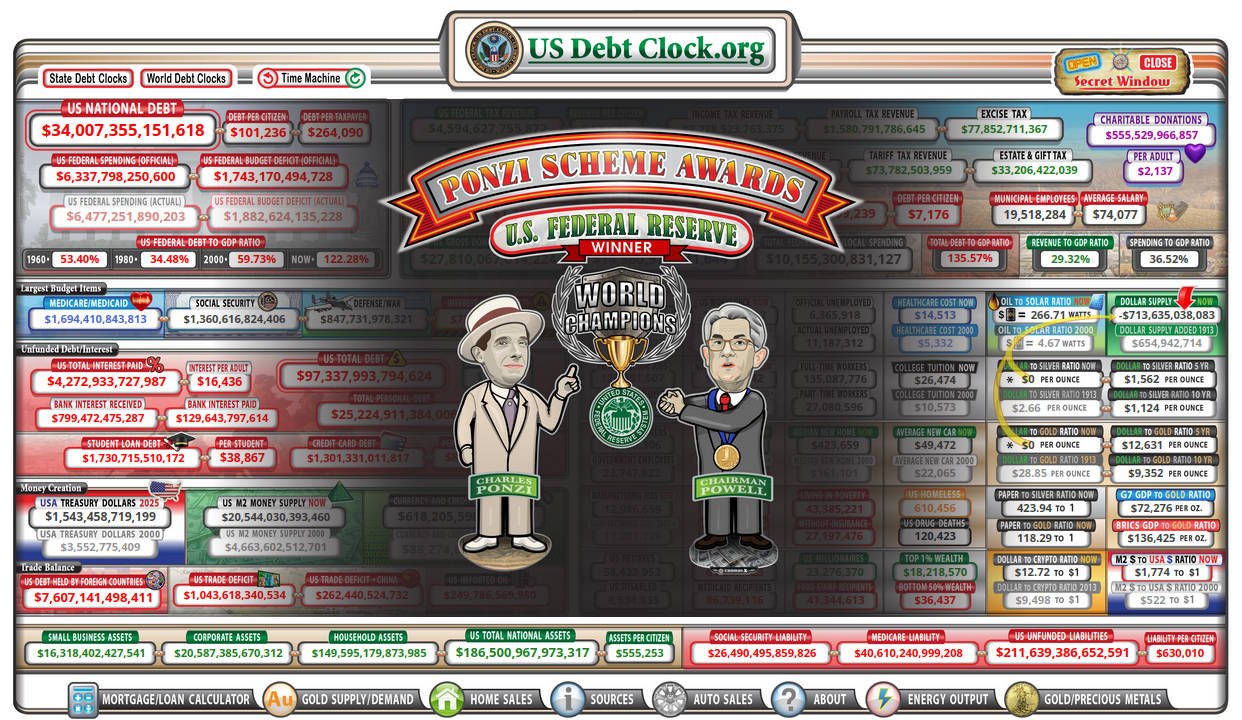
Central Bank Ponzi Schemes: A Look at How Long They’ve Been Around
Central Bank Ponzi schemes have been around for centuries, with the earliest known instance dating back to the 1600s in Italy. Since then, several other countries have experienced central bank Ponzi schemes as well, including France, Germany, and the United States. Despite the long history of such schemes, their modern form and effects on the economy have been largely understudied—until recently. Central bank Ponzi schemes are a form of fraud, which involves artificially inflating the value of a currency by creating false demand for it. This is done by using newly-created money to purchase existing currency, thereby creating a false sense of scarcity that drives up prices. The scheme works by using newly created money to purchase existing currency, thus creating a false demand and driving up its value. This results in a temporary increase in the value of the currency, until the scheme collapses and the currency’s value plummets. The effects of these schemes can be devastating, as they can lead to rapid inflation and devaluation of the currency. This can have dire consequences for an economy, as it can lead to high levels of unemployment, widespread poverty, and economic instability. While the
How the Central Bank Ponzi Scheme Has Ripped Off the World’s People for Decades
Since its creation in the 1940s, the Central Bank Ponzi Scheme has been a major part of the global financial system, allowing governments and financial institutions to reap huge profits at the expense of the world’s people. What is the Central Bank Ponzi Scheme, and how has it been exploiting the public for decades? At its core, the Central Bank Ponzi Scheme is a system of fractional reserve banking, wherein banks are allowed to lend out more money than they actually have on deposit. This is made possible by the fact that most people only make withdrawals of a small fraction of their deposits, allowing the banks to keep the rest and lend it out. As more and more people deposit money into the bank, the amount of money lent out increases, generating more profits for the bank. This is where the Central Bank Ponzi Scheme comes in. When the banks lend out more money than they have on deposit, the Central Bank steps in and provides the extra funds. This allows the banks to continue their lending operations and generate more profits. The problem is, the Central Bank is only able to do this because it prints additional money, which devalues the currency and causes inflation. This means that the value of people’s money is decreased over time, and they get less buying power for their money. The Central Bank Ponzi Scheme has been going on for decades and has had a profound impact on the world’s people. It has allowed governments and financial institutions to make huge profits while the value of people’s money has been steadily eroded. This has led to increased inequality, poverty, and economic instability around the world. The Central Bank Ponzi Scheme is an example of how the world’s financial system can be rigged to benefit a privileged few at the expense of everyone else. It’s time for governments and financial institutions to take responsibility for the harm they have caused and find ways to make the system fairer and more equitable. Only then can we ensure that the world’s people are able to benefit from a financial system that works for everyone.
Examining the Central Bank’s Unsustainable Monetary System
The current monetary system of the central bank is unsustainable and must be addressed in order to protect the economy from further damage. The central bank’s monetary system is based on a fractional reserve system, which is a system where banks are required to hold only a fraction of the deposits they receive as reserves. This system is not sustainable and is leading to an instability in the economy, as banks are unable to meet the demands of their depositors. Banks are also unable to meet the demands of their borrowers, due to the lack of liquidity in the system. The fractional reserve system creates an environment of uncertainty, as banks are unable to predict how much liquidity they will have in the future. This leads to banks taking on more risk, which can result in an increase in defaults and bankruptcies. This is due to the fact that banks cannot predict the future level of liquidity and are forced to take on more risk in order to cover any potential losses. The instability in the economy is further compounded by the central bank’s monetary policy. The central bank sets interest rates and controls the money supply, which can lead to an increase in inflation. The higher inflation can lead to a decrease in the value of the currency and can make it difficult for businesses to operate. The unsustainable monetary system of the central bank must be addressed in order to ensure that the economy remains stable. The central bank must implement measures to ensure that banks are able to meet their obligations to their depositors and their borrowers. This can be done by increasing the reserve requirement, which will increase the amount of money that banks must keep on hand in order to meet their obligations. In addition, the central bank must implement measures to control inflation. This can be done by increasing the interest rate, which will make it more expensive for businesses to borrow money. This will help to reduce the amount of money that is available for businesses to borrow, which will help to reduce the amount of money in circulation and help to reduce the level of inflation. The central bank must also ensure that the money supply is kept at a stable level. This can be done by adjusting the money supply in response to changes in the economy. This will help to ensure that the money supply remains at a level that is conducive to economic growth and stability. In conclusion, the central bank’s unsustainable monetary system must be addressed in order to ensure that the economy remains stable and is able to grow. The central bank must take measures to increase the reserve requirement, raise interest rates, and adjust the money supply in order to ensure that the economy remains stable and that businesses can operate without fear of inflation or an increase in defaults.
How the Central Bank’s Ponzi Scheme Has Eroded Financial Stability
The financial system of a nation is a delicate balance of investments, savings, and transactions. In order to maintain a level of stability, the central bank is responsible for providing a secure and trustworthy environment for banking, investment, and other financial activities. Unfortunately, the recent proliferation of central bank ‘Ponzi schemes’ has had a deleterious effect on financial stability, leading to significant losses and a lack of trust in the banking system. A Ponzi scheme is a fraudulent investment operation which employs existing funds from investors to pay off earlier investors, rather than generating income from any legitimate sources. In the case of central banks, these schemes are sometimes used to finance deficits or to expand the money supply to increase spending in an economy. By issuing bonds, the central bank is able to attract more investors and generate more money, creating the illusion of a profitable business. However, this is not sustainable in the long run and eventually the scheme collapses, leaving investors with huge losses. The central bank’s Ponzi scheme has had a number of damaging effects on financial stability. First, those who have invested in the scheme have been left with large losses, eroding confidence in the banking system and leading to a decrease in investment. Second, by using existing funds to pay off earlier investors, the central bank is essentially devaluing money, leading to inflation and reduced purchasing power. Third, because the scheme is not sustainable in the long run, it leaves the central bank vulnerable to defaults and lenders may be unwilling to extend credit in the future. In order to maintain financial stability, it is essential that central banks exercise extreme caution when engaging in any form of Ponzi scheme. Not only are such schemes unethical and potentially illegal, they also can have a devastating effect on the economy and the banking system. It is essential that central banks take the necessary steps to ensure that all banking activities are transparent and legitimate in order to maintain trust and financial stability.
The Need to Transition Away From Central Bank Ponzi Schemes
In recent years, there has been an increasing recognition of the need to transition away from central bank Ponzi schemes. This is due to the fact that these schemes are inherently unstable and create a wide range of negative economic and social consequences. A Ponzi scheme is an investment fraud that involves promising investors large returns based on the money of subsequent investors. Central banks, by definition, are controlled by a government and are responsible for the monetary policy of a nation. In a central bank Ponzi scheme, the government uses newly printed money to pay investors, and the money created is not backed by any economic activity or real economic value. As such, the money created is essentially worthless and the scheme is not sustainable in the long term. The negative consequences of a central bank Ponzi scheme are numerous. Firstly, the newly printed money causes inflation, as it increases the money supply without being supported by any real economic growth. This can lead to a rapid devaluation of the currency, which reduces purchasing power and purchasing confidence. Secondly, the scheme creates wealth inequality, as the investors at the top of the pyramid benefit the most, while those at the bottom suffer the most when the scheme collapses. Finally, the scheme can lead to significant levels of debt, as the government must continually issue more money to pay investors in order to keep the scheme going. The challenges of transitioning away from central bank Ponzi schemes are significant, but there are a number of solutions that can be employed. Firstly, governments should focus on increasing economic growth, as this will provide a more sustainable source of money to pay investors. Secondly, governments should focus on reducing public debt, as this will reduce the need for creating new money and will be more sustainable in the long term. Finally, governments should focus on creating financial regulations that will discourage irresponsible behaviour and prevent the creation of such schemes in the future. In conclusion, it is clear that the need to transition away from central bank Ponzi schemes is urgent. These schemes have a wide range of negative consequences, and the longer they continue, the more difficult it will be to escape them. Fortunately, there are a number of solutions that can be employed to help transition away from such schemes and create a more sustainable economic system.
What Alternatives to Central Bank Ponzi Schemes Exist and How Will They Be Adopted?
The current economic system is held up by central bank-backed Ponzi schemes, which are unsustainable and often detrimental to the economy. Fortunately, there are several viable alternatives that can be adopted to replace this system. First, governments can look to implement a “gold standard” monetary system, which would peg the value of a currency to a commodity, typically gold. This would help to stabilize the economy and reduce the risk of inflation, as the money supply would be backed by a physical asset. However, this type of system is only feasible if there is a large enough supply of gold available to back the money. Second, governments can move to a system of “commodity-backed money”, which would involve the backing of a currency by a basket of commodities, including but not limited to gold, silver, oil and other goods. This would help to reduce the risk of inflation and create a more stable economic environment. Third, governments can look to a “fiat money” system, which would involve the issuing of currency not backed by any physical asset. This would provide more flexibility in the money supply and help to reduce the risk of inflation. The downside, however, is that it would require a great deal of trust in the government to maintain the value of the currency. Finally, governments can look to a “cryptocurrency-based” system, which would involve the use of digital currencies such as Bitcoin. These currencies are not backed by any physical asset, but are instead based on an open, decentralized ledger system. This system would help to reduce the risk of inflation by providing a more stable and secure form of money. The adoption of any of these alternatives will depend on the willingness of governments to make a change from the current system of central bank-backed Ponzi schemes. It is likely that the most successful system will be one which is able to provide the most stability and security for the economy, while also providing the necessary flexibility.