In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the promise of artificial intelligence (AI) is met with an escalating concern: the vulnerability of AI systems to cyberattacks. Recently, the U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) unveiled a report on “Trustworthy and Responsible AI,” shedding light on the persistent challenges in defending AI systems from malicious actors. The report identifies four types of cyberattacks that could manipulate the behavior of AI systems, urging the community to devise more robust defenses.
The threats of adversarial machine learning
The NIST report delves into the intricacies of adversarial machine learning, categorizing potential attackers into three distinct types: white-box hackers, sandbox hackers, and gray-box hackers. White-box hackers possess full knowledge of AI systems, sandbox hackers have minimal access, and gray-box hackers hold partial information about an AI system but lack access to its training data. Despite their varying degrees of insight, all three pose serious threats to the integrity of AI systems.
Fraud in the digital realm is on the rise, as pointed out by Gerhard Oosthuizen, CTO at Entersekt. The technology that initially promised wins now presents more challenges in the face of growing sophistication in fraudulent activities. The NIST report underscores the escalating risks as AI becomes increasingly embedded in our connected economy.
The report highlights two primary adversarial machine learning attacks: poisoning and abuse. AI system poisoning involves injecting corrupted data during the training phase, leading to malfunctioning systems. The NIST cites an example where a bad actor introduces inappropriate language into conversation records, causing a chatbot to adopt these instances as common parlance in customer interactions.
On the other hand, abuse attacks involve inserting incorrect information into a legitimate source that the AI system absorbs. These attacks aim to repurpose the AI system’s intended use by providing it with incorrect pieces of information. Alina Oprea, a co-author of the NIST report and a professor at Northeastern University, notes the simplicity of these attacks, requiring minimal knowledge and adversarial capabilities.
Cyberattacks unveiled – Navigating AI’s defense complexity
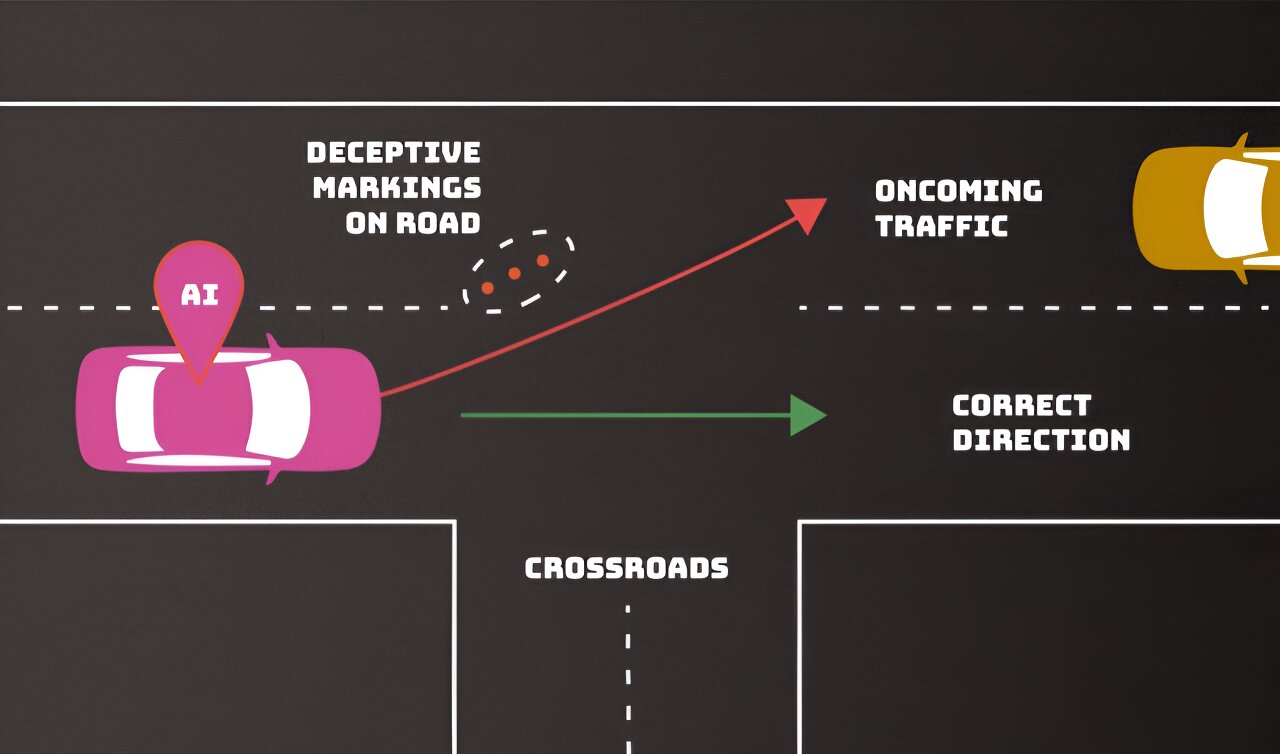
Privacy attacks and evasion attacks add further layers of complexity to AI defense. Privacy attacks attempt to glean sensitive information about the AI or its training data, using legitimate questions to reverse engineer the model. Evasion attacks, occurring after deployment, seek to alter the AI system’s responses to traditional inputs. This includes deceptive modifications to road signs, posing risks to autonomous vehicles.
The overarching challenge lies in the difficulty of making AI models unlearn taught behaviors, even when they prove malicious or damaging. As AI becomes more ingrained in our daily lives, the report warns of the growing necessity to address these vulnerabilities to prevent catastrophic failures.
As the specter of cyberattacks looms over the advancement of AI, the NIST report brings attention to the unresolved challenges in securing AI systems. The call to the community for better defenses underscores the urgency of addressing these vulnerabilities. Can the AI community collectively devise foolproof measures to safeguard against evolving cyber threats, or are we destined to navigate the ever-expanding maze of adversarial machine learning attacks? The future of AI defense rests on our ability to innovate and stay one step ahead of those seeking to exploit its vulnerabilities.