As the popularity of the blockchain industry and the crypto market continues to grow, many developers and investors are looking for the best platform to build and invest in.
While Ethereum has been the leading platform in this field for many years, other blockchains, such as Polygon (formerly Matic Network), are gaining ground.
But what distinguishes them? Which one fits your needs the best? We will compare “Polygon vs Ethereum” in this blog article, discussing their features, blockchain architecture, and use cases.
Polygon vs Ethereum: Overview
| Polygon (MATIC) | Ethereum (ETH) | |
| Launched date | 2017 | 2015 |
| Market Cap | $220B | $9B |
| Transaction Speed | 7,000 TPS | 15-25 TPS |
| Transaction Costs | Low | High |
| Block time | 2 seconds | 15 seconds |
| Block Size | 50 KB – 2 MB | Dynamic |
| Number of network validators | 100 | >220,000 |
| Ecosystem Apps | ~200 | ~4,000 |
| Consensus Algorithms | Hybrid PoS | PoS |
Polygon vs Ethereum: History and Background
Vitalik Buterin founded Ethereum in 2015 as a blockchain platform that quickly gained widespread recognition for its innovative features, such as the ability to develop decentralized applications and smart contracts. The platform’s native digital currency, Ether (ETH), has since emerged as the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization.
Polygon, on the other hand, was launched in 2017 as Matic Network to solve the scalability issue of Ethereum. It was created by a team of developers led by Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, and Anurag Arjun.
In 2021, it rebranded itself as Polygon and became an independent blockchain network while still being interoperable with Ethereum.
Technical Differences between Polygon and Ethereum Network
Breaking down the technical differences and exploring features, working, and network architecture of two leading blockchain technology platforms.
1. Polygon vs Ethereum: Consensus Mechanism
Polygon operates on a hybrid Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. It combines the benefits of PoS and checkpointing. Checkpointing provides additional security by periodically taking snapshots of the network’s state and anchoring them to the Ethereum mainnet. The approach makes it more difficult for attackers to manipulate the network’s history.
Ethereum is currently using a pure PoS consensus algorithm through its Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. It is more energy-efficient and less costly than Bitcoin’s PoW.
PoS allows users to validate transactions and create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency (in this case, MATIC or ETH) they hold.
2. Polygon vs Ethereum: Smart Contract Language
Polygon is a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum that supports Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatible smart contracts. It uses Solidity to write smart contracts and supports other programming languages like Vyper. Its SDK is written in Golang, an open-source programming language.
Ethereum executes smart contracts using its native programming language Solidity. It allows for creating dApps that can perform various tasks, from simple transactions to complex computations.
3. Polygon vs Ethereum: Transaction Speed (TPS)
Polygon offers faster transaction speeds than the Ethereum network. It can achieve up to 7,000 transactions per second (TPS) on its mainnet, while Ethereum can only process around 15-25 tps.
However, Polygon’s theoretical transaction throughput is 65,000 TPS, which is 4000 times faster than the Ethereum blockchain. But it is still a theoretical assumption. It’s practically impossible due to increasing network traffic.
4. Polygon vs Ethereum: Gas Fees (Transaction Fees)
Based on recorded gas fees, the Polygon network generally has faster and cheaper transactions than Ethereum. The transaction costs on Polygon are around 0.1-0.5 MATIC, while that on Ethereum is around $2.5-$20 or equivalent ETH. These numbers can vary significantly depending on network congestion and high transaction demand.
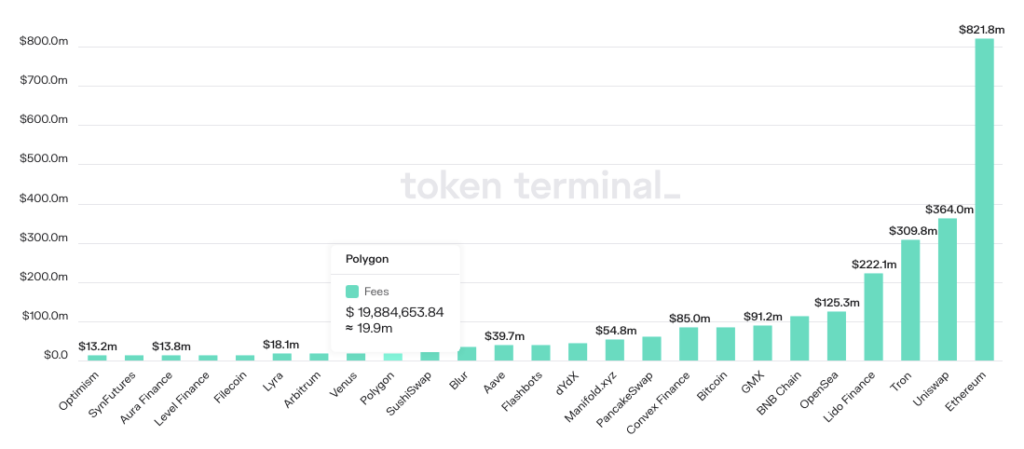
According to Token Terminal data, The fee collected on the Polygon blockchain is around $19.9m, with Ethereum being the highest fee collector, around $821.8m.
5. Polygon vs Ethereum: Network Security & Decentralization
Ethereum’s PoS consensus mechanism is considered to be secure and has over 220,000 validators. This makes it a completely decentralized system.
On the other hand, Polygon’s hybrid PoS consensus algorithm and stateful architecture is also considered to be secure with 100 validators. This number set is still considered to be partially decentralized due to the distribution of validators across different geographies and organizations.
6. Polygon vs Ethereum: Interoperability
Interoperability is the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate and interact with each other.
Ethereum has been a pioneer in this space, with many other blockchain networks being built on top of it. Its ERC-20 standard has become the industry standard for creating new tokens.
Polygon is also compatible with Ethereum. This makes it easy for developers to migrate their existing dApps and tokens from Ethereum to Polygon.
MATIC vs ETH: Market Cap and Tokenomics
The market capitalization of ETH is approximately USD 220 billion, making it the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization after Bitcoin. The market capitalization of MATIC, on the other hand, is around USD 9 billion.
ETH has a maximum supply of 120.4 ETH, while MATIC has a circulating supply of 9.92 billion tokens, with tokens being released gradually over time through a process called token release.
Polygon vs Ethereum: TVL and DApps Ecosystem
Total Value Locked (TVL) and the number of Decentralized Applications (DApps) are key indicators of the success and adoption of any blockchain platform.
TVL refers to the total amount of assets locked in smart contracts on a blockchain platform.
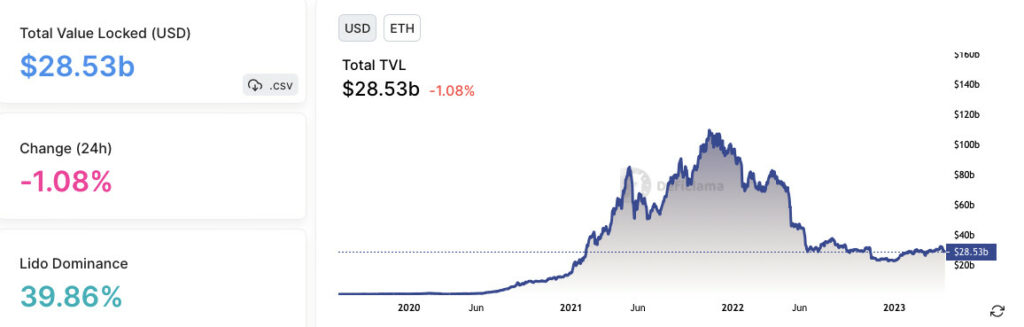
According to Defillama, Ethereum has been the dominant player in the TVL space for a long time, with a current TVL of over $28.53 billion.
It has also been the leader in the DApps ecosystem, with over 4,000 DApps currently running on its network. The majority of these Ethereum ecosystem DApps are in the finance sector, with popular projects such as:
- Uniswap: Decentralized exchange protocol for trustless cryptocurrency trading.
- Aave: Lending and Borrowing platform with interest earning and collateralized borrowing.
- Lido DAO: Liquid staking service for earning rewards by staking ETH tokens.
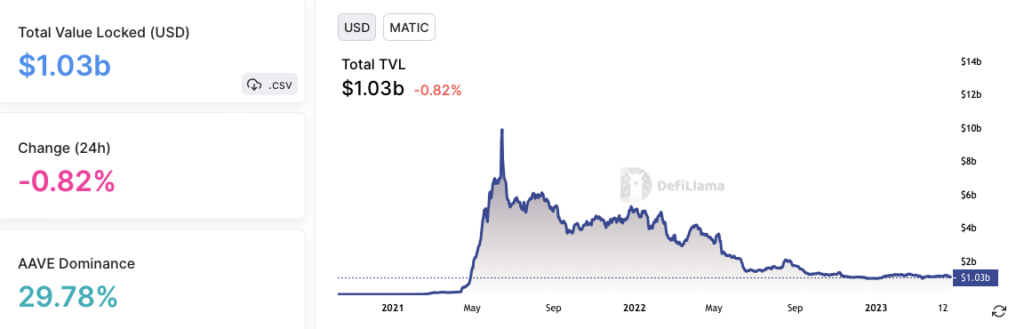
Polygon has a TVL of $1.03 billion and is dominated by Aave and Quickswap. The network currently hosts more than 300 DApps, primarily emphasizing interoperability.
While this number is significantly lower than Ethereum’s, it’s worth noting that Polygon’s focus is on providing faster and cheaper solutions for developers.
Polygon vs Ethereum: OpenSea NFTs
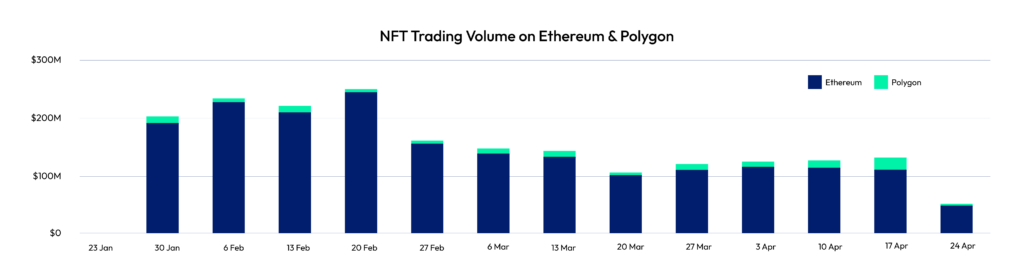
OpenSea is a popular NFT marketplace that operates on both MATIC and Ethereum networks, allowing users to buy and sell digital assets.
On OpenSea, Polygon NFTs are generally traded for GameFi and in-game assets, whereas Ethereum is popular for pixelated art collections and virtual real estate cards.
Here are some of the popular NFT Collections based on Opensea Stats. Top Polygon NFTs are:
- The Sandbox
- ZED Run
- CyberKongz VX
- MyCryptoHeroes
Ethereum is the preferred blockchain for NFTs, but its high gas fees discourage some users. However, as Polygon gains more high-profile partnerships with companies like Disney, Facebook, etc., it is becoming more popular.
Top Ethereum NFTs are:
- Bored Ape Yacht Club
- Otherdeed for Otherside
- Azuki
- Clone X
According to Cryptoslam, Opensea sold more than 1.6 million NFTs on Polygon in January. This is a significant achievement since OpenSea has only sold around 1.08 million NFTs on Ethereum’s primary network.
Polygon vs Ethereum: Use Cases
Here are some use cases for each platform that can help businesses make informed decisions about which platform to use by blockchain developers.
Polygon Use Cases
- Gaming and Esports: One of Polygon’s most promising use cases is in the gaming industry. The platform’s fast and inexpensive transactions make it an ideal choice for in-game purchases and microtransactions, and several gaming companies have already started using Polygon.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Polygon’s architecture suits DeFi applications that require faster and cheaper transactions. Several popular DeFi protocols, including Aave and Curve Finance, have already migrated to Matic.
Ethereum Use Cases
- Decentralized Applications (DApps): From decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and social media platforms like Steemit to prediction markets like Augur, Ethereum has been used to build a wide range of innovative applications.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Ethereum is also the platform of choice for DAOs, which are organizations that are run by code rather than by humans. DAOs can be used for everything from managing investment funds to organizing political campaigns.
- Tokenization: It has been used to tokenize many assets, including real estate, commodities, and other cryptocurrencies.
What is Polygon (MATIC)?
Polygon is a Layer 2 scaling platform designed to enhance Ethereum’s efficiency and scalability as a blockchain network.
Its primary objective is to integrate multiple self-contained blockchains, known as “sidechains”, with Ethereum’s primary blockchain to create a more effective network. Each sidechain is tailored to the particular demands of various applications and can interconnect with other sidechains through the Polygon network.
Furthermore, the platform leverages several scaling solutions, including Plasma and Rollups, to augment its throughput and minimize transaction fees.
Recently, Polygon collaborated with Hermez Network to build polygon zkEVM. It combines zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to create a highly scalable and secure network.
Pros and Cons of Polygon
Pros of Polygon
- High throughput capacity
- Interoperability with the Ethereum blockchain
- Innovative solutions like “commit chains” that enable private transactions
- Low gas fees incentivize the adoption
- Strong focus on building Partnerships
Cons of Polygon
- Relatively untested in high-network congestion scenarios
- Limited decentralization compared to more established networks
What is Ethereum (ETH)?

Ethereum is a decentralized virtual machine that executes smart contracts on its blockchain. It has a vibrant developer community and is used for various purposes, such as DeFi, supply chain management, and identity verification.
Recently, it has transitioned from PoW to PoS consensus algorithms. This transition can improve network scalability and reduce energy consumption, making it more efficient and sustainable.
Pros and Cons of Ethereum
Pros of Ethereum
- Enables decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs)
- Supports the development of smart contracts
- A Platform for decentralized applications (apps)
- Creates unique digital assets like NFTs
- Allows participation in decentralized finance (DeFi)
Cons of Ethereum
- Limited scalability and high gas fees
- Difficulty in regulation and governance
Final Thoughts: Which Should You Choose?
In the beginning, you have many questions. How do they compare, Polygon vs Ethereum? Which blockchain is better for you? When choosing a blockchain platform, there are many factors to consider as a developer or investor.
Suppose you are looking for a more established and widely adopted platform with a higher degree of decentralization. In that case, Ethereum is better than Polygon. With its strong network effects, large developer community, and first-mover advantage, it remains the choice for building DApps and launching smart contracts.
On the other hand, if you prioritize speed, low transaction fees, and scalability, then Polygon is a great alternative. As a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum, Polygon offers faster and low gas fee transactions without compromising security or decentralization.
Moreover, Polygon’s interoperability with other chains and protocols makes it a versatile platform for cross-chain transactions and DeFi applications.
Learn more: Avalanche vs Ethereum (2023): Can Avalanche Surpass Ethereum?
Polygon vs Ethereum: FAQs
Which is the Better Investment, Polygon or Ethereum?
Ethereum has a significantly higher ROI of 64614.55% compared to Polygon’s 21411.02%. However, ROI alone should not be the sole factor for determining the better investment option.
Therefore, deciding between Polygon and Ethereum is crucial to evaluate the tradeoffs between a more established but less scalable platform versus a newer but more agile solution. It is also vital to consider the project’s specific needs and long-term goals.
How does Polygon stand out against the Ethereum blockchain?
Polygon is better than Ethereum blockchain because it can process transactions faster and at a lower cost.
It achieves this by using the Proof-of-Stake Checkpointing algorithm. These checkpoints serve as markers to verify the blockchain’s state at a particular time and help protect against long-range or double-spending attacks.
Will Polygon Compete With Ethereum?
Polygon can be seen as a complementary solution to Ethereum and is not necessarily positioned as a direct competitor.
The rise of Polygon has been nothing short of remarkable in recent years, with the platform garnering a significant amount of attention and adoption in the blockchain community. While there is no denying that Polygon’s popularity is on the upswing, it’s important to note that Ethereum still reigns supreme in use cases.
So, while Polygon may continue to gain ground and attract more users, it seems unlikely to displace Ethereum as the dominant force in space completely.