In an era where digital innovation shapes every facet of our lives, the emergence of large language models (LLMs) in artificial intelligence (AI) marks a transformative technological era. Pioneered by entities like OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic, these models redefine how we interact with and benefit from machine learning.
The essence of large language models
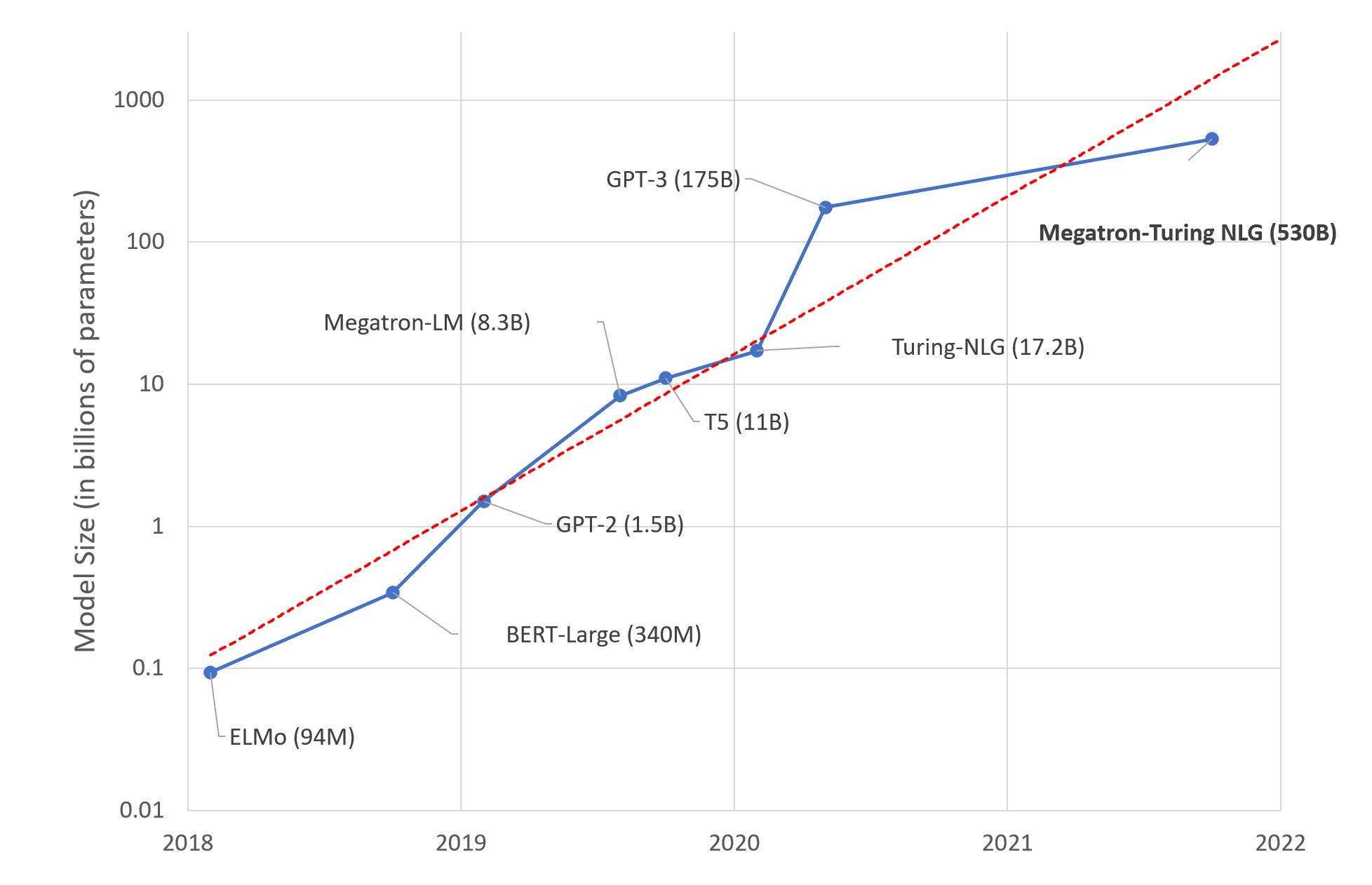
At their core, LLMs are sophisticated algorithms trained on extensive text datasets. Their primary function is to predict word sequences, enabling the generation of coherent and contextually relevant text. This process, unsupervised learning, equips the models with a nuanced understanding of language, encompassing grammar and stylistic elements. The evolution of these models from basic language processing tools to complex systems has been monumental. Groundbreaking models like Google’s Transformer have set the stage for more advanced iterations, including OpenAI’s Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) series. These models stand out for their ability to produce coherent and contextually accurate text, trained on diverse datasets from books, websites, and other written materials.
Applications and innovations
The applications of LLMs are vast and varied, cutting across multiple sectors. In education, they assist in creating and evaluating educational materials and tutoring students. The healthcare sector sees its use in interpreting clinical notes and researching medical literature. LLMs enhance market analysis, automate customer service, and streamline financial reporting in finance. The media and entertainment also utilize these models for content creation, scriptwriting, and personalizing recommendations.
Their capabilities extend beyond these practical applications. LLMs excel in generating narratives, articles, and poetry, showcasing a profound grasp of language structure. They also play a crucial role in language translation, sentiment analysis, and summarizing large volumes of text, demonstrating their versatility and utility in information synthesis.
Ethical implications and future directions
Despite their potential, LLMs present significant ethical challenges. One of the primary concerns is the risk of inheriting biases from their training data, highlighting the need for continuous efforts to ensure fairness. Privacy issues, particularly regarding using personal data in training, demand strict adherence to privacy laws and data anonymization practices. Other critical concerns include the potential for misuse in spreading misinformation and the implications of job displacement due to automation.
Looking forward, the future of LLMs is bright but requires careful navigation. Advancements in capabilities are anticipated, promising greater accuracy and versatility. However, addressing ethical challenges is crucial for responsible usage. Ongoing research focuses on enhancing efficiency, reducing biases, and improving interpretability. Efforts are also underway to develop less resource-intensive models for greater accessibility and environmental sustainability.