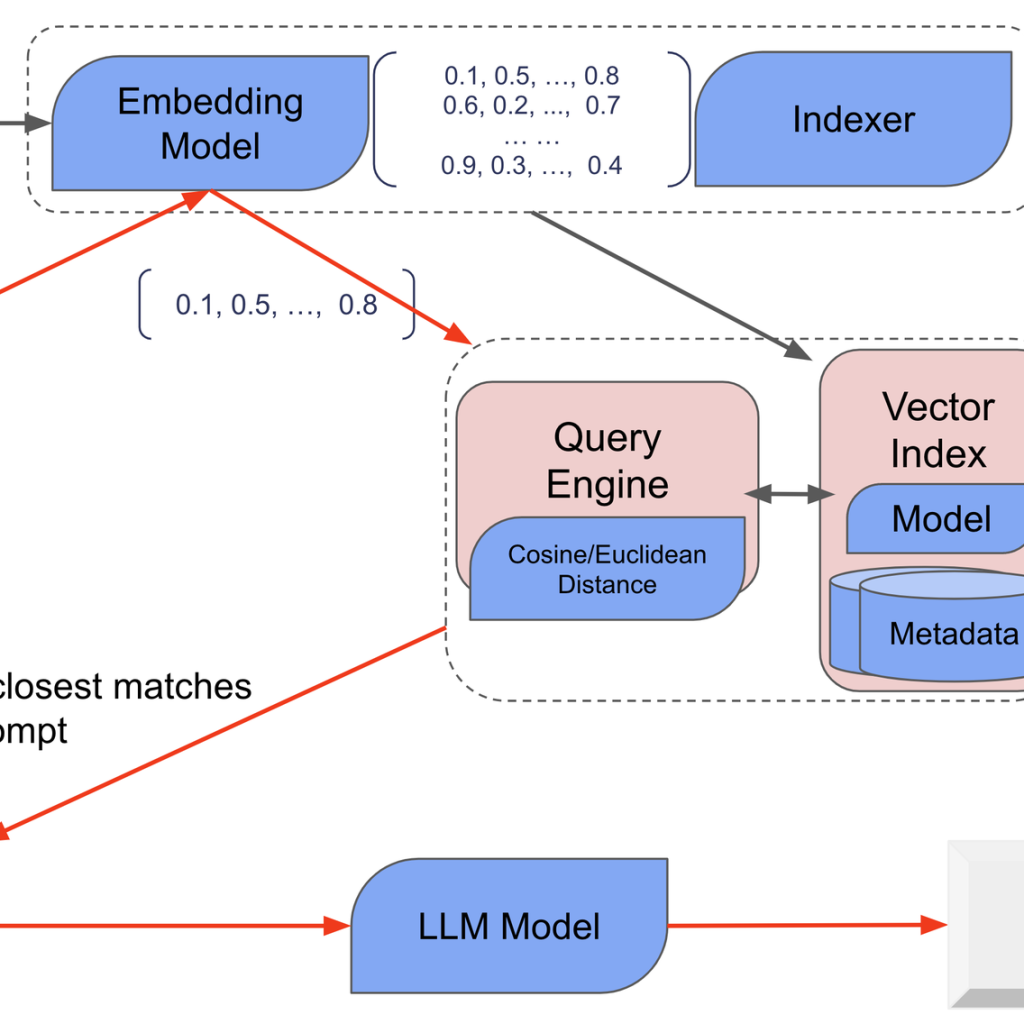
In a bold and thought-provoking critique, Joseph Shieber challenges the prevailing narrative surrounding artificial intelligence (AI) and its applications, proposing a fundamental reevaluation of terminology and conceptualization.
Shieber argues that the current nomenclature misrepresents the nature and capabilities of what is commonly referred to as “artificial intelligence” systems, particularly Large Language Models (LLMs).
Redefining LLMs: Genuine tools, not artificial
Shieber’s first contention challenges the very terminology used to describe these systems. Drawing parallels with commonplace appliances like washing machines and cars, Shieber posits that labeling LLMs as “artificial” is a misnomer.
Unlike fake or phony constructs, LLMs are genuine aids designed to simplify and enhance human endeavors. Their advancements in understanding and language comprehension, as noted in recent studies, underscore their tangible utility.
The fallacy of “Artificial Intelligence”
Shieber contends that the term “artificial intelligence” itself is misleading, as it implies a level of cognitive capability that LLMs do not possess. While acknowledging the significant strides made by LLMs, Shieber asserts that intelligence is an ongoing process rather than a static attribute. He refutes arguments based on consciousness, embodiment, and experience, instead focusing on the nature of intelligence as a collective, evolutionary pursuit guided by institutions.
Debunking Misconceptions: Intelligence vs. Prediction
Central to Shieber’s argument is a crucial distinction between the goals of human intelligence and LLMs. While human intelligence aims at truth-seeking through testing and iteration, LLMs prioritize predicting responses based on existing data.
Shieber posits that LLMs excel at generating plausible responses akin to human answers rather than accurately representing reality. This critical difference undermines their classification as intelligent entities.
Shieber’s critique challenges conventional wisdom and sparks a reevaluation of how society perceives and labels advancements in artificial intelligence. By reframing LLMs as genuine tools and emphasizing their predictive rather than truth-seeking nature, Shieber offers a nuanced perspective that prompts deeper reflection on the nature of intelligence and technology’s role in shaping human endeavors.
Implications for future development
Shieber’s analysis carries significant implications for the ongoing development and deployment of AI technologies. By recognizing the limitations of current terminology and conceptual frameworks, researchers and policymakers can adopt a more nuanced approach to AI governance and ethics.
Shieber’s call to reassess the goals and capabilities of LLMs encourages a shift towards more transparent and responsible AI development practices.
Redefining AI calls for a paradigm shift
Joseph Shieber’s critique challenges prevailing notions of artificial intelligence, advocating for a reevaluation of terminology and conceptual frameworks. By reframing LLMs as genuine tools and emphasizing their predictive nature, Shieber prompts a deeper understanding of the goals and limitations of AI technologies.
As society continues to grapple with the implications of AI, Shieber’s insights offer a valuable perspective for navigating the complex intersection of technology and human intelligence.