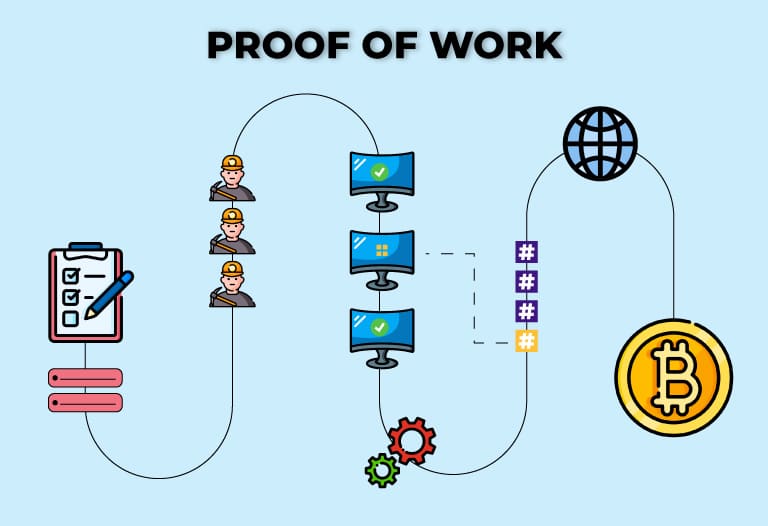
In the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrencies, the concept of decentralization stands as a cornerstone, and at the heart of this decentralized revolution is Bitcoin. Amidst various consensus mechanisms, Proof of Work (PoW) has emerged as the stalwart force that not only powers the Bitcoin network but also ensures its resounding decentralization. In this blog post, we delve into the pivotal role that Proof of Work plays in keeping Bitcoin decentralized and secure.
The Essence of Decentralization:
Preserving Autonomy:
At its core, decentralization in the context of Bitcoin refers to the distribution of power and control across a vast network of participants. This design ensures that no single entity or authority has undue influence or dominance over the network, preserving the autonomy of its users.
Trustless System:
Decentralization also embodies the concept of a trustless system, where users can transact and interact without relying on intermediaries or central authorities. Bitcoin’s decentralized nature is a direct response to the vulnerabilities associated with centralized systems, offering a peer-to-peer, censorship-resistant alternative.
The Role of Proof of Work:
Mining as the Decentralizing Force:
Proof of Work, the consensus algorithm underpinning Bitcoin, relies on miners to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. Mining is a decentralized process where participants, known as miners, compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets the right to add a new block and is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins.
Competitive Mining Landscape:
The competitive nature of mining ensures that power is distributed across a vast network of miners globally. This prevents any single entity from controlling the majority of the network’s mining power, maintaining a level playing field for participants irrespective of their size or resources.
Security through Difficulty:
The difficulty adjustment mechanism in PoW plays a crucial role in maintaining a consistent block time. As more miners join the network, the difficulty increases, making it harder to mine a block. Conversely, if miners leave, the difficulty decreases. This self-regulating mechanism ensures that the block time remains relatively constant, contributing to the security and stability of the network.
Decentralization Challenges and Solutions:
Threats to Decentralization:
While PoW is a robust mechanism, challenges such as mining centralization and environmental concerns have been raised. Concentration of mining power in certain geographic regions or by specific mining pools poses a potential risk to decentralization.
Ongoing Innovations:
The Bitcoin community, ever committed to maintaining decentralization, actively explores solutions to address these challenges. Initiatives like mining pool decentralization, the development of more energy-efficient mining hardware, and the exploration of alternative consensus mechanisms are ongoing endeavors.
Conclusion:
Proof of Work stands as the bedrock of Bitcoin’s decentralized architecture, ensuring that power is distributed, transactions are secure, and users can engage in a trustless system. While challenges persist, the resilience of the Bitcoin community in addressing these issues underscores the commitment to preserving the essence of decentralization.
Stay tuned to BitlyFool.com for in-depth explorations of the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrencies. As we navigate the complexities of blockchain technology, Proof of Work remains a testament to the enduring principles of decentralization that define the ethos of Bitcoin.